Defining a blockchain can be as hard as any other cryptocurrency subject. Still, today, we will give you the most basic definition possible to reach the highest level of understanding without getting too geeky in the process – what is blockchain and how does blockchain work?
What is Blockchain?
The blockchain is a technology based on a peer-to-peer communication network. Blockchain, as its name, means a Chain of Blocks. It is an immutable, decentralized, secure, and distributed database that maintains a continuously growing list of chronological records called blocks. Each block contains a timestamp and a link to the previous block.
History of Blockchain
In 2008, Nakamoto published a paper on The Cryptography Mailing list describing the digital bitcoin currency.
As a part of the Bitcoin implementation, they also devised the first blockchain database, which serves as the public ledger for all transactions. In the process, they were the first to solve the double-spending problem for digital currency.
Although Bitcoin uses a Blockchain, Blockchain ≠ Bitcoin.
Working Principle of Blockchain
Thinking of a ledger is the best way to explain what a blockchain is and what it does. Some transactions will go on that ledger when any movement is done with cryptocurrency. So, the blockchain is the way to keep records of the transactions that are made with these virtual currencies. There are no bank accounts or physical versions, but everything is recorded in these blockchains to keep track of all cryptocurrency movements.
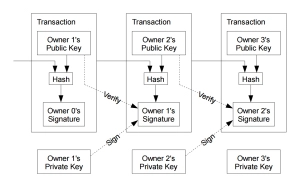
The Blockchain System
The blockchain is not any giant supercomputer that takes care of everything. Instead, a large number of nodes contribute to the process of maintaining and running the blockchain to ensure a secure environment that is not corruptible. Security breaches could be present in any virtual environment, but the security measures applied in blockchains are pretty sturdy. It’s hard for anyone to be able to hack their way into a system that uses this practical and superior technology. The number of people getting involved grows daily, and business ventures accepting payments with these virtual currencies are also increasing. Part of the trust comes from a highly efficient system.
Where is it useful?
Since Blockchains consist of an openly distributed ledger, they can be verified permanently by a network, so they are secure by design and highly tolerant of inconsistencies. Therefore, it is possible to achieve a decentralized consensus with a Blockchain. That makes Blockchains very ideal for:
- Medical Records
- Identity Management
- Transaction Processing
- Digital Currencies
- Payment Systems
- Governance (Voting Systems)
- Crowdfunding
- Proving data lineage
- Peer-to-Peer Insurance
- Internet of Things
- Stock Trading
- Land Title Registration
- Freight Tracking
Who can contrast its ease of availability to traditional ownership records, such as those hosted by Banks, where only the Bank has control over the ledger? That reduces the costs of verifying transactions by removing the need for trusted third parties (such as Banks) to complete transactions.
The Future of Blockchain
There is very little doubt in most people’s minds that we are going to enter a whole new stage in a few years where most business owners are going to have big signs on their doors that read “We take Cryptocurrency,” and that future is much nearer than most people think or consider.



